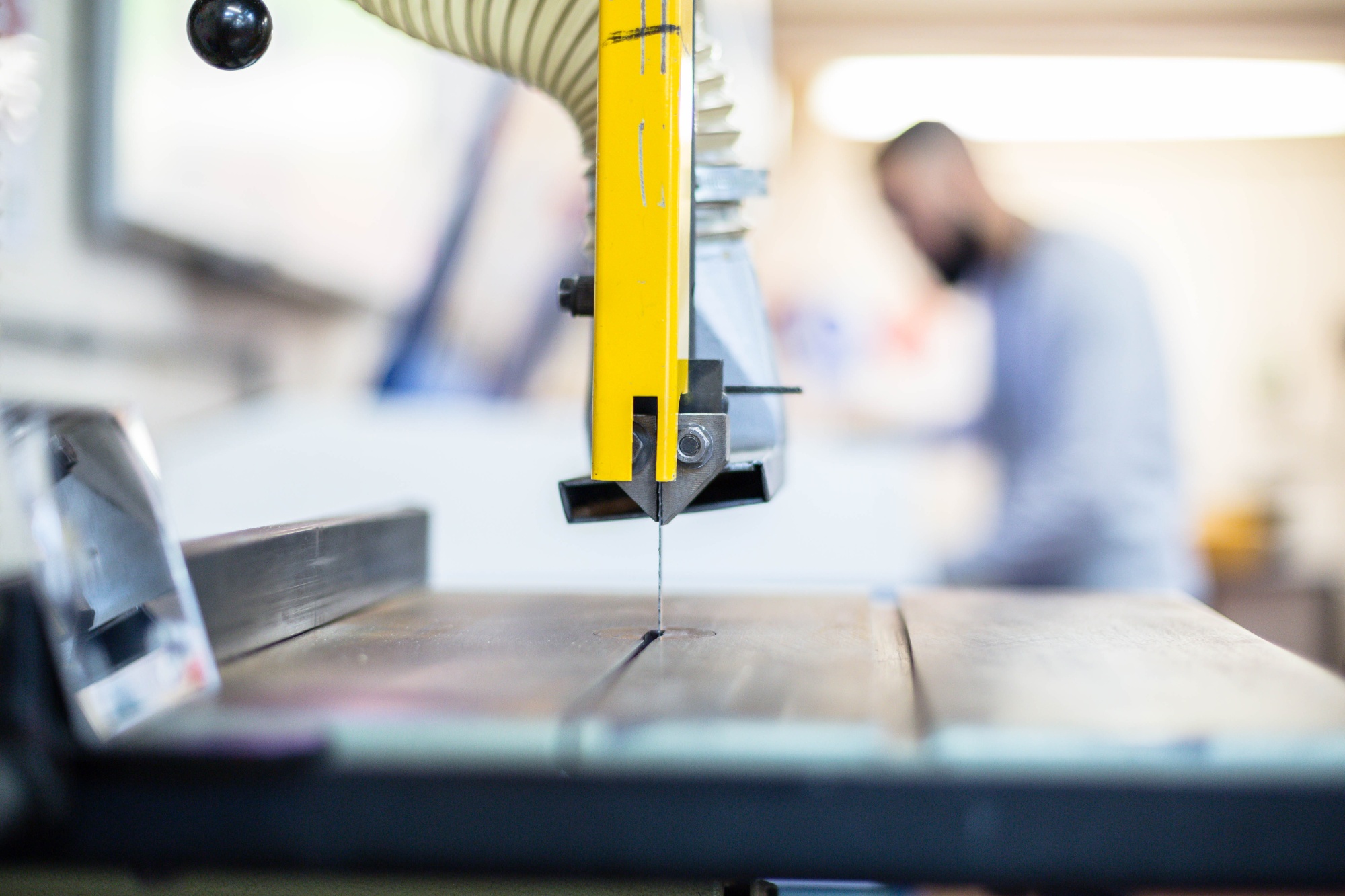
Why study Design Technology?
“It’s not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works”
Steve Jobs, 2003
Everything around us from the food we eat and the clothes we wear to the buildings we live in has been produced by design and technological activities.
The study of Design Technology (DT) is a highly exciting and relevant subject that enables students to make sense of and understand the technologies enjoyed by our society today.
DT aims to give students the skills to thrive, adapt and participate creatively in technologies which are still evolving while also highlighting the environmental responsibilities associated with design.

Key Stage 3
Key Stage 3 (KS3) Design Technology is a 3-year programme that introduces students to the areas of Design and Technology offered by the department, currently Product Design (PD), Systems and Control, Graphics and CAD/CAM.
The aim of KS3 is to provide an enjoyable, comprehensive and relevant foundation course giving students the confidence to work safely, skilfully and independently in all DT contexts. Girls are introduced to the basic skills, processes, materials and terminology used to manufacture products and pro-actively to respond to problems and identified needs.
An appreciation of the need for environmental responsibility when making design or consumer decisions is promoted, enabling students to make informed choices.
DT offers the opportunity to develop many other transferable skills through a range of problem solving design-and-make projects in a cross curricular and collaborative environment. eg creative thinking, planning, product analysis and research. Currently the DT course is structured to enable students to work collaboratively with Food Technology, Electronics and Product Design.
The current Year 7 course is themed ‘Myself in our technological world’. Product Design students manufacture plastics, learn basic mechanical control and the graphic skills to express their creativity when problem solving.

The theme for Year 8 DT is ‘Meeting the needs of other people’. In Product Design students manipulate machines to shape wood and learn about basic electrical control systems.
During Year 9 students explore the needs of industry in detail using a range of production methods to produce DT products from metal in quantity.
Key Stage 3 Product Design


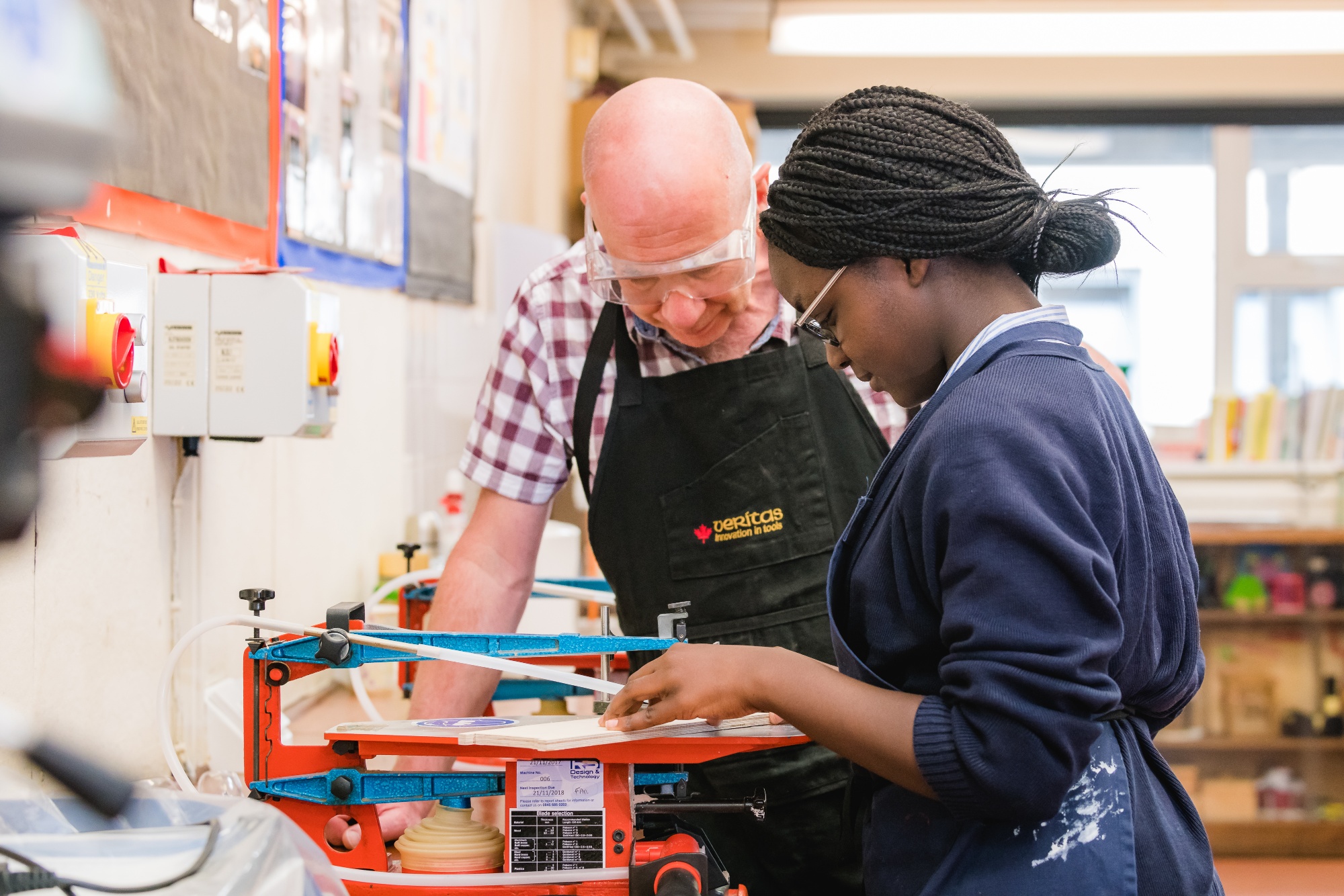
Key Stage 3 Electronics
Students will gain various skills throughout the projects undertaken in Key Stage 3. They will be able to use their computational thinking to program models and kits. Students will also develop the ability to use the correct technical knowledge of basic electronics components and the correct symbols when using circuits. Students will understand how advanced electronic systems can be powered and used in products. They will apply computing and use electronics to embed intelligence in the product that respond to inputs and control output using programmable components. Students will also learn to appreciate the importance of working in a team and in a professional manner, as well as to become more independent learners.
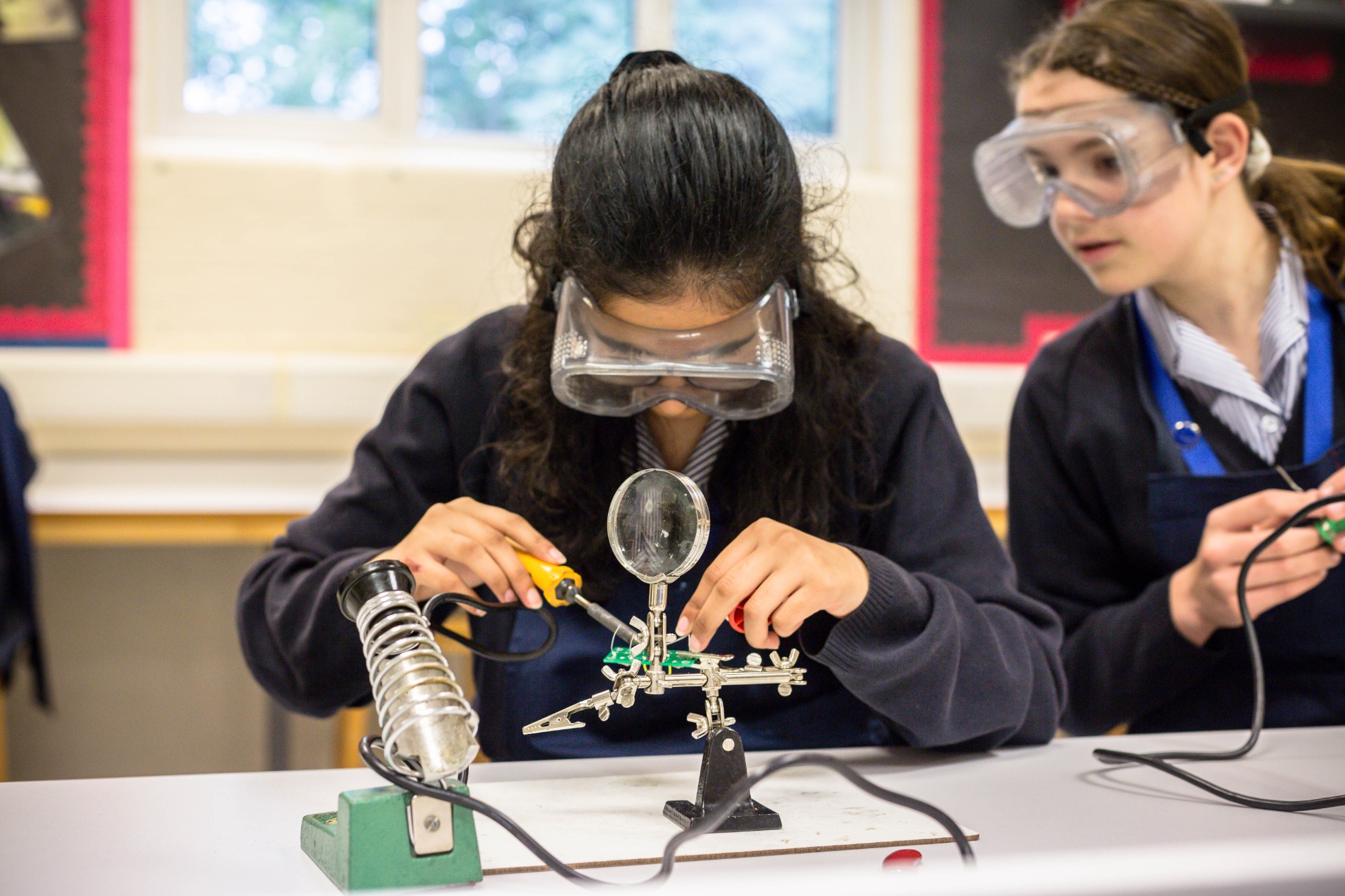

Key Stage 4
GCSE Design & Technology [AQA]
‘Design is a process and a way of thinking. From kitchenware to software and from health to high street fashion, design thinking leads to creative solutions that impact on every area of our lives’.
Newson, Suggett, Sudjic. 2016.
Overview:
The Study of Design & Technology at GCSE level will help students to develop a set of creative, transferable life skills that will help them to participate, navigate and influence a 21st century that is increasingly complex, technologically driven, and difficult to predict.
Students will gain an awareness of and learn from wider influences on Design and Technology, including historical, social, cultural, environmental and economic factors. Students engage with the iterative processes of design, to problem find and problem solve, to generate innovative and creative solutions in response to a design brief.
Course Structure:
Theory = 50%
Theory is studied throughout year 10 and 11 and culminates in a two-hour written exam at the end of year 11. Examination questions cover: Core technical principles; specialist technical principles; designing and making principles.
NEA [Non-exam assessment] 50%
Students undertake a single ‘design and make’ activity, which will arise from investigating a contextual challenge. This involves the production of a portfolio of work, which will consist of: investigation and research; design ideas; design development; modelling; testing and evaluation. The portfolio of work will inform the production of a prototype that satisfies the design brief and is fit for purpose.
The NEA begins just after the May half term in year 10 and concludes just before Easter in year 11.
Requirements:
To succeed at GCSE level, you need to be good at the four C’s: Creativity, Collaboration, Communication and Critical thinking. You also need to:
Be interested in:
Products, systems and the built environment; the creative processes of design; designing and making products; materials and their working properties; practical processes – using tools, machines and equipment.
Have aptitude for:
Investigating problems; asking questions and looking for solutions; generating and communicating ideas through drawing; discussing ideas and embracing feedback from others; developing ideas through dialogue, drawing and modelling; realising ideas through planning and making.
Be willing to:
Proactively think and work in an independent way; manage your time and meet deadlines; reflect upon, evaluate and question your work constantly; gather information and compile a portfolio; embrace the uncertainty that creative freedom brings.
Examples of student work:
Contextual Challenge: ‘Addressing the needs of people with disabilities’ [2019].
A product to help elderly people cross the road and be more visible to oncoming traffic.
Contextual Challenge: ‘Supporting developing countries’ [2019].
A product to help young girls in developing countries cook more safely on an open fire.
Key Stage 5 Design Technology
We stage a number of opportunities to enable students to continue DT activities at KS5 both formally and informally.
Each year a significant number of Graphic students continue their interest in design by opting to study A Level Art.
A popular courses in Product Design is available for students who may have dropped DT at the end of KS4 but would enjoy spending time pursuing creative and practical projects on an informal basis.
There is a further avenue for students to further explore an interest in design with the production of a private study project.
Enrichment activities at Woodford
Students at Woodford are regularly given the opportunity to get involved in a wide range of DT extracurricular activities.
Each year National Design Week is celebrated by a KS 3-4 design competition.
Master classes have been held by visiting architects, garden designers and chefs allowing Year 9-11 students the inspiring opportunity to have focussed experience of experts in their particular field of design.
Graphics students have visited The Design Museum, The Packaging Museum and the V&A to take part in hands-on workshops.
The Year 7s had success with a product design competition run by Practical Action, and other competitions include participating in local Rotary technology tournaments.
Future Pathways:
Studying Design & Technology provides a vital ‘stepping-stone’ towards numerous future pathways, all linked to the creative professions and industries, including Architecture, Design and Engineering.
Career possibilities include:
Architecture; Engineering; Product Design; Graphic Design; Interior Design; Systems Design; Web Design; Digital Design; Information Design; Fashion Design; Textiles Design; Landscape Design; Transport Design; Lighting Design; Furniture Design; Construction; Manufacturing; Making and Building.
If you are interested in studying Design & Technology at GCSE level, please contact Mr Baines.